TYPES OF PATIENTS WITH HYPOTHYROIDISM
Some patients with hypothyroidism can be challenging to treat and require special consideration. Use this section to review the cases of Steve, Jennifer, and Diana to see how to effectively manage their hypothyroidism with Synthroid (levothyroxine sodium).

Steve, 50
Recently diagnosed patient*
- Recently diagnosed with hypothyroidism
- Initiating treatment

Jennifer, 32
Pregnant patient*
- Diagnosed with hypothyroidism 3 years ago
- Started and managed on levothyroxine

Diana, 70
Elderly patient*
- Diagnosed with hypothyroidism 10 years ago
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) diagnosed 6 months ago
*Hypothetical patient profiles.
Recently diagnosed patient

Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
- Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantiu.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde
Steve is a 50-year-old man with hypothyroidism.

Past Medical History:
- 4 months ago, 190-lb patient complained of fatigue, dry skin, constipation, cold intolerance, TSH 10.2 mIU/L, BP 150/60, total cholesterol 235 mg/dL; patient was diagnosed with hypothyroidism and started on Synthroid 100 mcg
- 8 weeks later, patient’s complaints continued. TSH 4.6 mIU/L; Synthroid dose increased to 125 mcg
Current Complaint:
- Nervousness, agitation, palpitations, and feeling hot for the past few months
Current Medications:
- Synthroid 125 mcg
Notable Physical Exam and Lab Findings:
- Sweating profusely despite air-conditioned exam room
- TSH 0.3 mIU/L
Diagnosis:
- Patient is displaying symptoms of being overreplaced with current dose of Synthroid of 125 mcg; TSH test confirmed
Treatment Plan Considerations:
- Decrease dose of Synthroid
- Recheck TSH levels in 4-6 weeks
CLINICAL INSIGHT
- Managing hypothyroidism requires frequent monitoring
PERCENTAGE OF PATIENTS TAKING THYROID MEDICATION WHO DO NOT ACHIEVE OPTIMAL EUTHYROID16,5
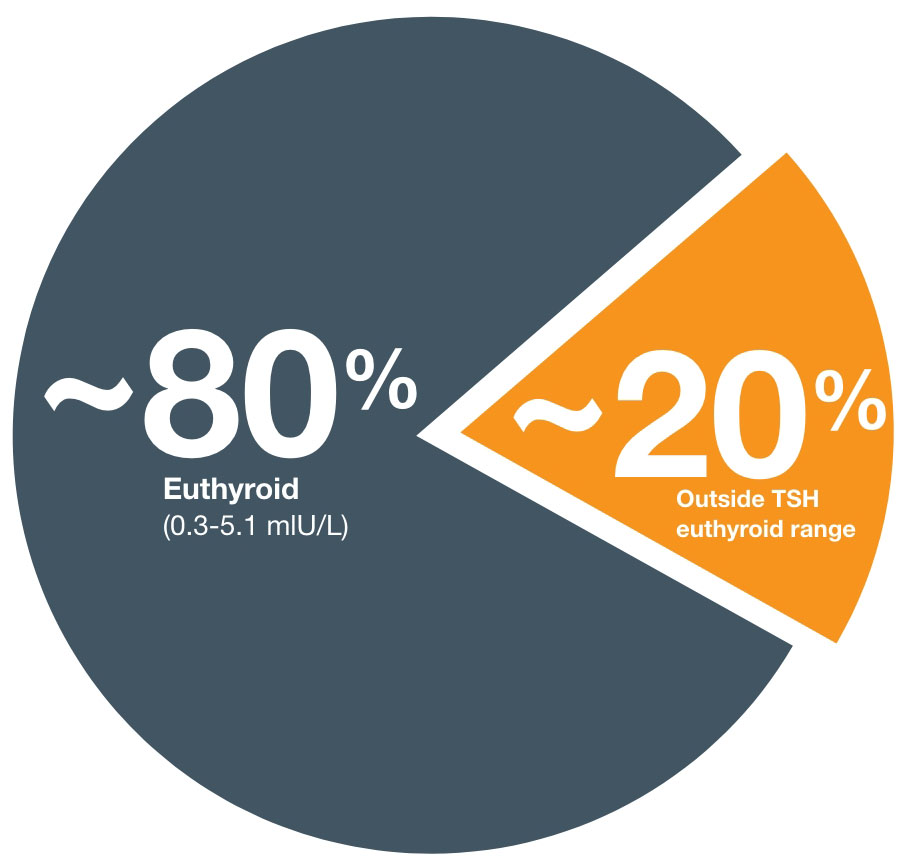
A retrospective Treatment Adequacy study was conducted between 2013-2020, and found that almost 20 years later, ~20% of patients taking thyroid medications still do not achieve normal TSH levels5
Overall, 81.1% ([Cl: 80.4; N=81.8]; N=9130) of patients had normal mean TSH levels, and 11.7% [Cl: 11.1-12.3; N=1312] and 7.3% [Cl: 6.8-7.8; N=817] had high and low TSH levels, respectively5
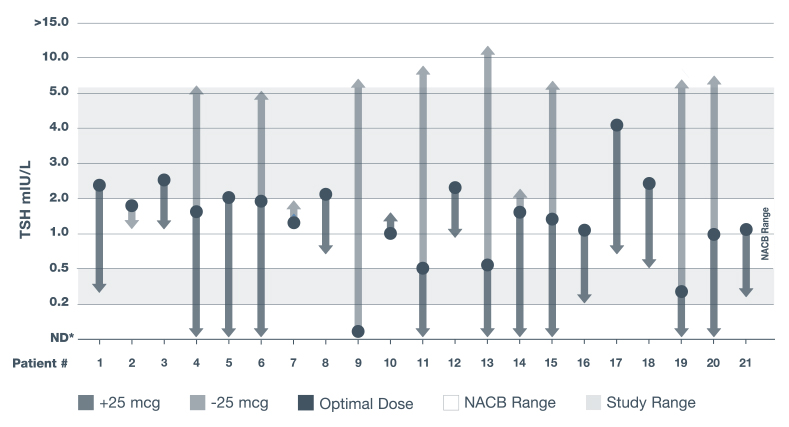
THE CARR STUDY: PROOF THAT PRECISE DOSING MATTERS17
Adapted from a 1988 biochemical study conducted in 21 adult Caucasian patients in the United Kingdom with primary hypothyroidism who were tested on a series of different thyroxine dosages to evaluate effectiveness of measuring TSH levels to monitor thyroid function.16
Following a 25-mcg dose change of levothyroxine, most patients had changes in TSH levels.
Pregnant Patient

Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
- Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantiu.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde
Jennifer is a 32-year-old woman in her first trimester of pregnancy with
hypothyroidism that is managed on Synthroid.

Past Medical History:
- Diagnosed with hypothyroidism 3 years ago
- Started and managed on 50 mcg Synthroid
- Weight fluctuation
- Appendectomy
Current Complaint:
- Fatigue and facial puffiness
Current Medications:
- Synthroid 50 mcg
Notable Physical Exam and Lab Findings:
- Young woman with cold, dry skin and facial puffiness
- TSH 6.2 mIU/L
Diagnosis:
- Patient is displaying symptoms of hypothyroidism due to subtherapeutic dosing of Synthroid; TSH test confirmed
Treatment Plan Considerations:
- Increase dosage of Synthroid
- Recheck TSH levels in 4 weeks
CLINICAL INSIGHT
TSH levels may increase during pregnancy. TSH should be monitored and Synthroid dosage adjusted during pregnancy.
- 2017 ATA Guidelines state that:
Between 50% and 80% of treated hypothyroid women need to increase their levothyroxine dosing during pregnancy18
ELDERLY PATIENT

Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo.
- Nemo enim ipsam voluptatem quia voluptas sit aspernatur aut odit aut fugit.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantiu.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accntiu.
Section Header
- Sed ut perspiciatis unde
Diana is a 70-year-old woman who has a history of hypothyroidism that has been managed
on 125 mcg of Synthroid for the past 5 years.

Past Medical History:
- Hypothyroidism diagnosed 10 years ago
- GERD diagnosed 6 months ago
Current Complaint:
- Increasing hair loss, fatigue, chronic constipation for the past few months
Current Medications:
- Synthroid 125 mcg
- Daily fiber supplements
Notable Physical Exam and Lab Findings:
- Well-nourished elderly woman with thinning hair
- TSH 8.5 mIU/L
Diagnosis:
- Patient is displaying symptoms of hypothyroidism (TSH test confirmed), most likely due to the concurrent use of daily fiber supplements
Treatment Plan Considerations:
- Counseled patient to take Synthroid on an empty stomach and at least 4 hours before or after other medications
- Recheck TSH levels in 6-8 weeks
CLINICAL INSIGHT
- Certain medications, supplements, and foods can affect absorption of levothyroxine, including Synthroid
Levothyroxine should be taken on an empty stomach and at least 4 hours before or after medications known to interfere with absorption1
Dietary fiber may bind and decrease the absorption of levothyroxine from the gastrointestinal tract1
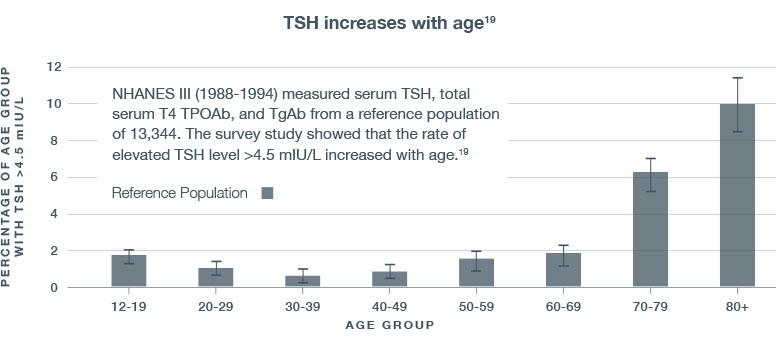
- The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) data have shown that the rate of elevated TSH (>4.5 mIU/L) increased with age19